Mobile software developers, whether working on iOS or Android, often use GPS functionality in their apps without fully understanding how GPS works. This article is designed to give you a basic understanding of GPS hardware, so you can appreciate the underlying technology and improve your app’s location-based features.
This article is structured as a conversation between an iOS developer (Alex 👨🏻💻) and an electrical engineer (Sarah 👩🏼💻). Through their dialogue, we’ll explore the fundamentals of GPS technology.

The Basics of GPS
👨🏻💻: So what does GPS stand for?
👩🏼💻: It stands for Global Positioning System.
👨🏻💻: Who created it, and for what purpose?
👩🏼💻: The GPS project was launched by the United States in 1973 to overcome the limitations of earlier navigation systems.
👨🏻💻: I know GPS works without an internet connection, but do I need cellular service to use GPS?
👩🏼💻: No, you don’t need cellular service either.
How GPS Works Without Internet or Cellular Service
👨🏻💻: How does GPS work without internet or cellular service?
👩🏼💻: Your device receives signals from satellites. There are about 24 operational satellites in six orbital planes.
👨🏻💻: Does my mobile need to connect to all of these satellites?
👩🏼💻: No, when stationary, your device only needs to receive signals from at least three satellites. When moving, it needs signals from four satellites for accurate positioning.
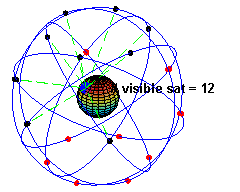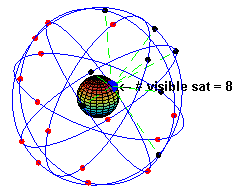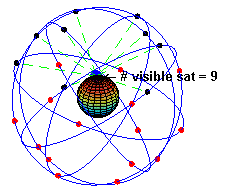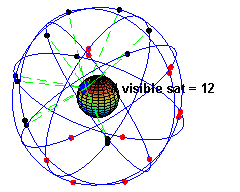
GPS Satellites in Orbit (Source: Wikipedia)
👨🏻💻: How does the GPS system identify me and send data back?
👩🏼💻: The satellites don’t identify you. They continuously emit synchronized pulses everywhere. Your device simply receives these signals.
Calculating Your Position
👨🏻💻: How does my mobile determine my latitude, longitude, and altitude?
👩🏼💻: Your device compares the time it receives signals from each satellite. By calculating the time differences, it can determine your position on Earth. The satellites have highly accurate atomic clocks, which make these calculations possible.
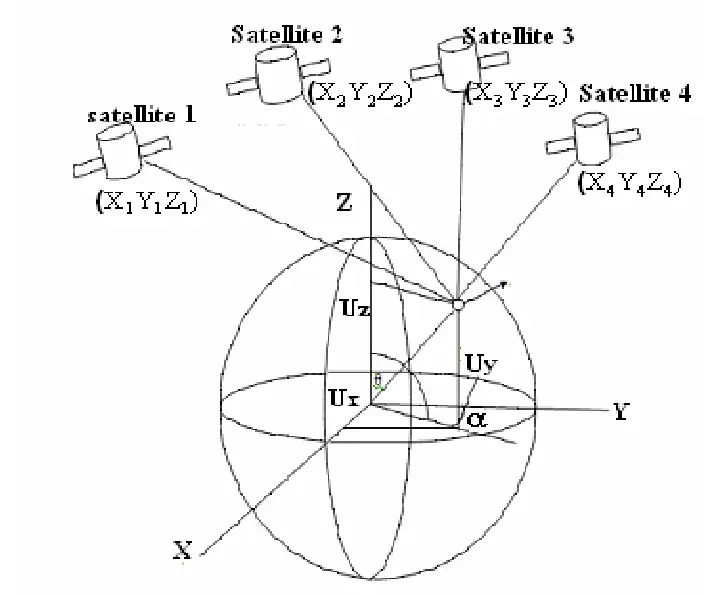
Calculating Position Using GPS Satellites
👨🏻💻: If the service is free and I don’t have a subscription for GPS, how is it funded?
👩🏼💻: GPS is one of several Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). Others include GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. These systems are funded by governments and sometimes private entities. Commercial GPS receivers might have restrictions, like not functioning at high speeds.
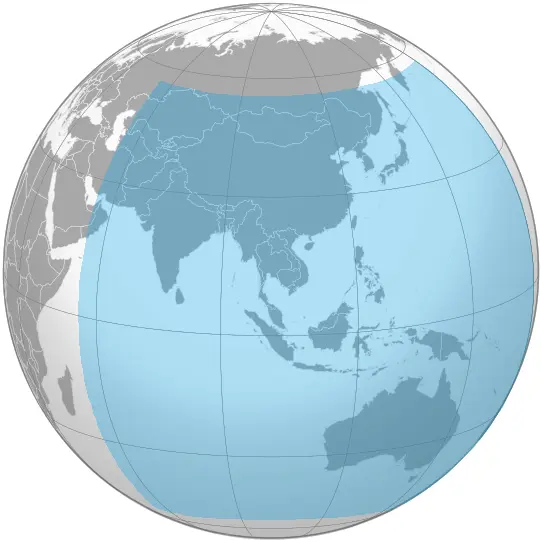
BeiDou GNSS, which doesn't have full Earth coverage
Accuracy and Limitations of GPS
👨🏻💻: What is the typical error margin of GPS?
👩🏼💻: The error margin varies but is typically between 15 to 50 meters. Some systems use additional inertial sensors to provide more accurate positioning.
👨🏻💻: What is the minimum detectable distance?
👩🏼💻: Theoretically, the resolution is as fine as one inch, but in practice, it’s about three meters.
Challenges of Using GPS Indoors
👨🏻💻: I tried using GPS inside a large hospital, but the readings were inaccurate.
👩🏼💻: GPS signals do not work well indoors because they require a clear line of sight to the satellites.
👨🏻💻: But I still got some readings on my maps app indoors.
👩🏼💻: That’s likely the last known location. Some devices, like those from Huawei, augment GPS data with accelerometer and gyroscope data to simulate basic indoor navigation, but it’s not reliable.
👨🏻💻: What technologies are used for indoor navigation systems?
👩🏼💻: Indoor navigation typically uses beacons, Bluetooth, and other technologies. You might want to look into Apple AirTags for more information.
Using Sensors for Positioning
👨🏻💻: Why can’t we just use the accelerometer and gyroscope in our phones to calculate position?
👩🏼💻: While you can derive some positional data from these sensors, they are prone to significant errors over time due to factors like drift and gimbal lock. Accelerometers and gyroscopes alone can’t provide absolute positioning, and their errors accumulate quickly.
👨🏻💻: That was a lot of information. Thanks for the explanation.
👩🏼💻: You’re welcome! See you soon.
Conclusion
Understanding how GPS works can help mobile developers better utilize location services in their apps. Whether you’re developing a navigation app or just curious about the technology behind the blue dot on your map, a basic knowledge of GPS hardware can enhance your approach to location-based features.

